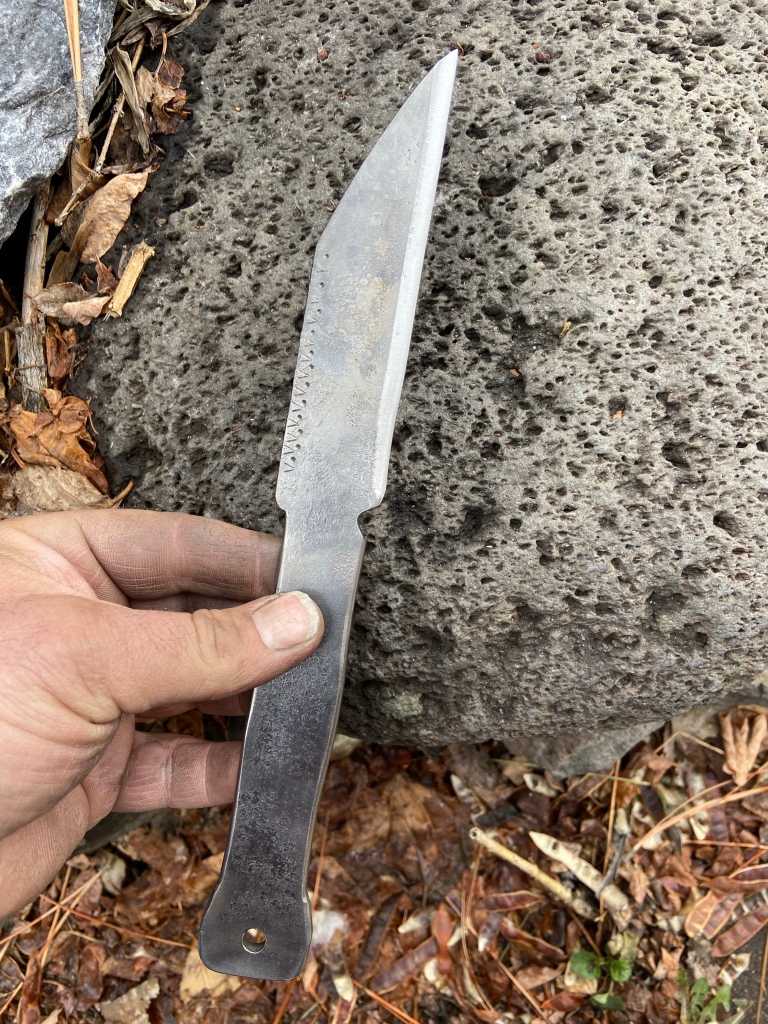
Dithmarschen Mjönir
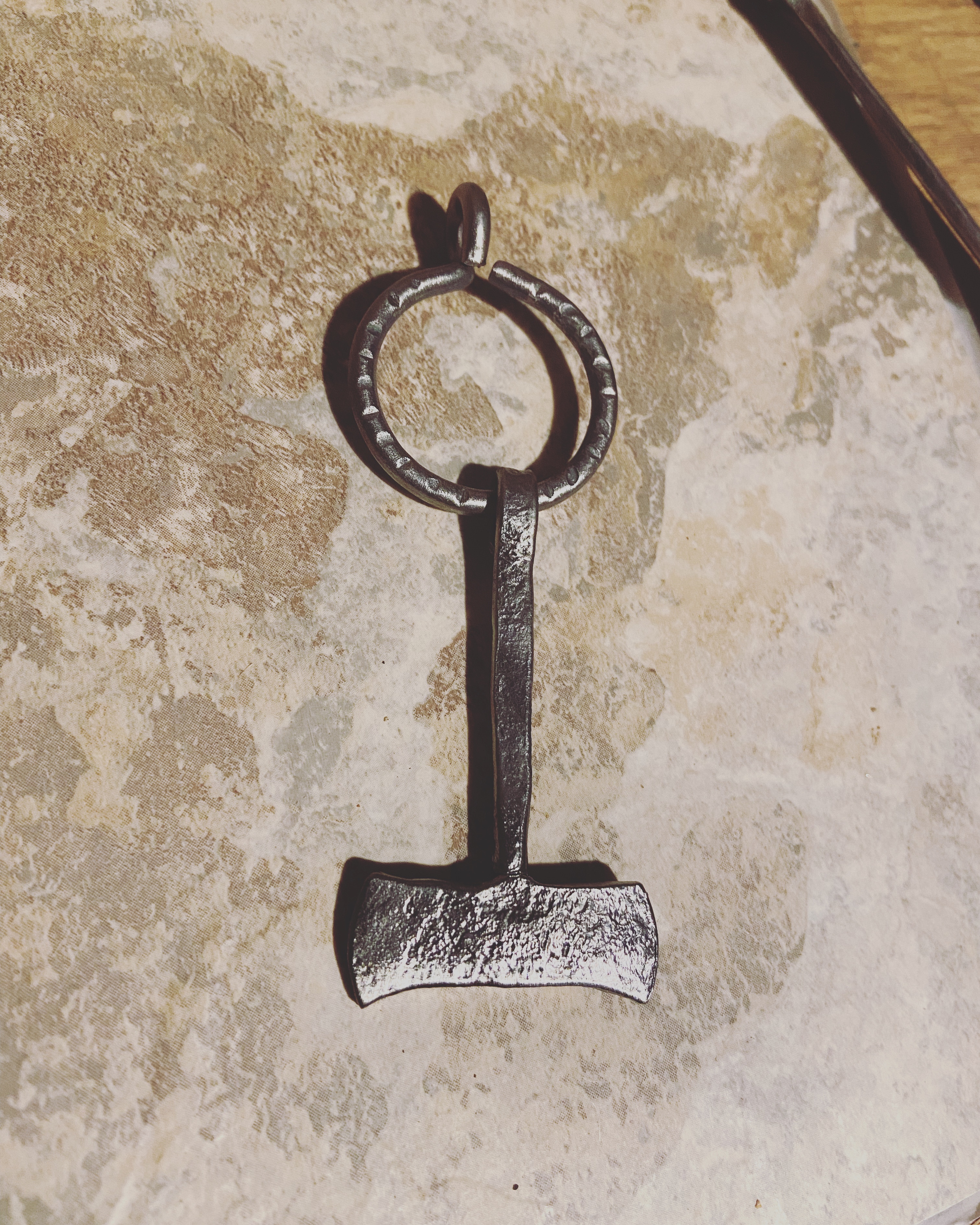
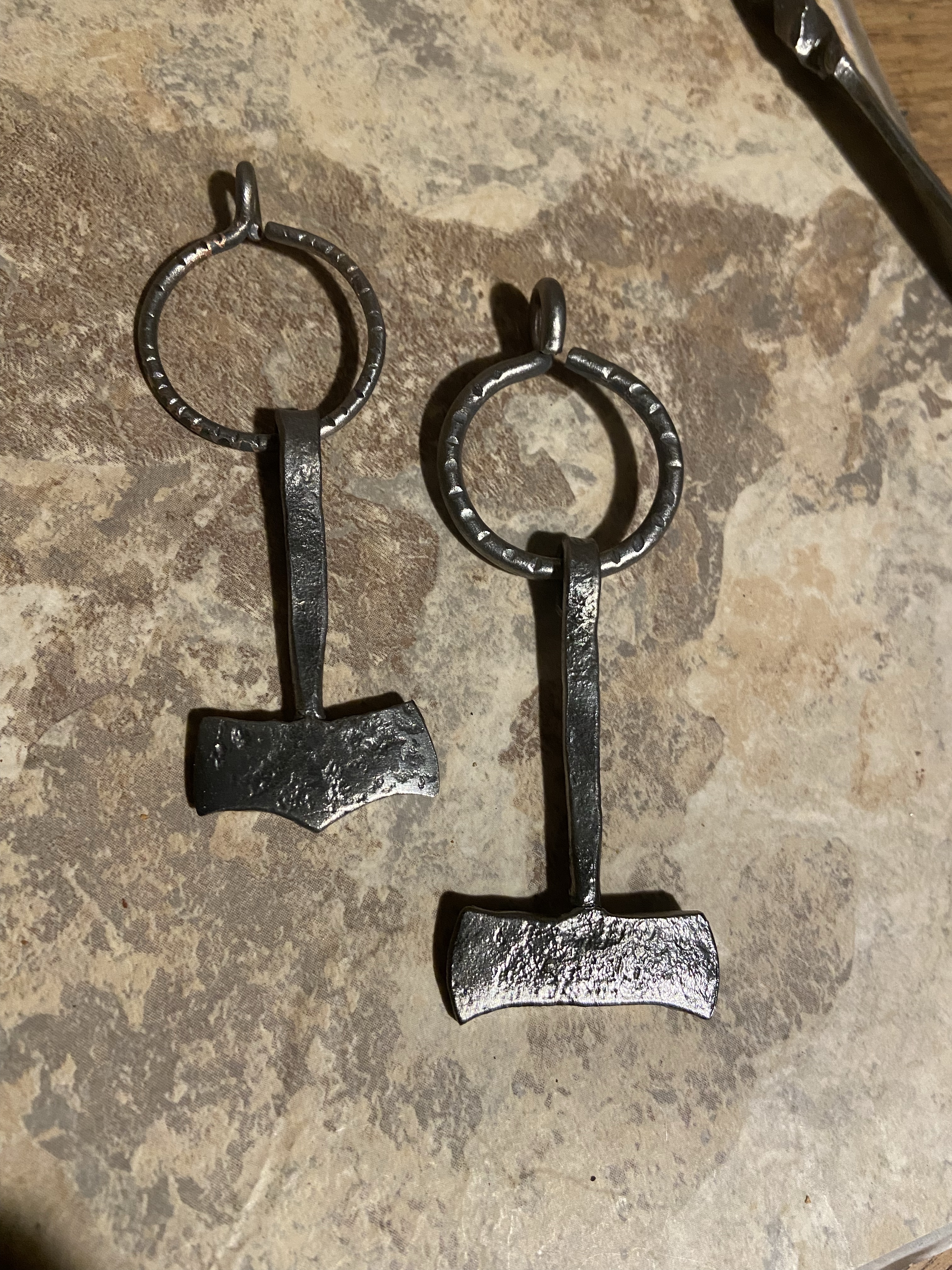
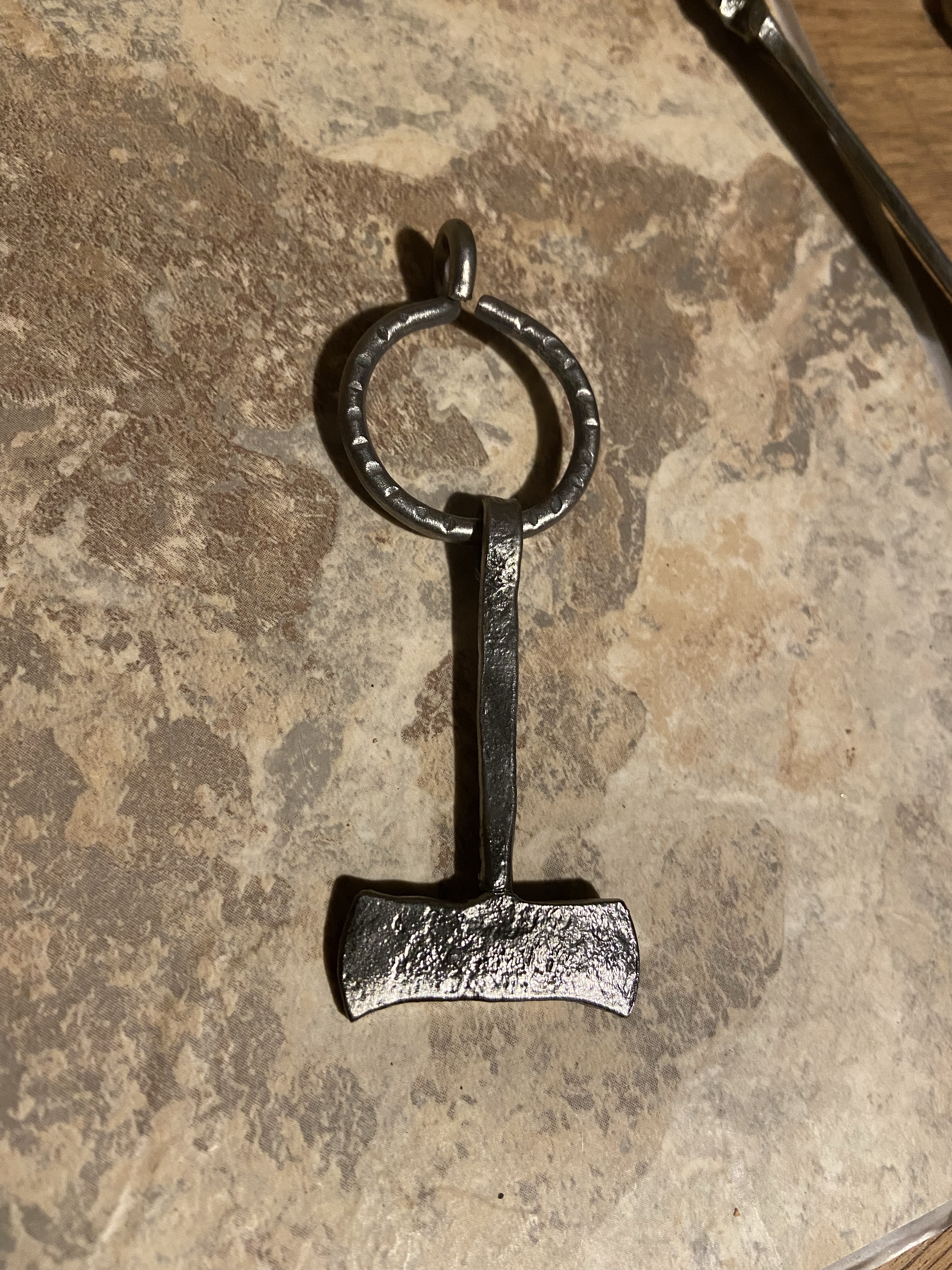





Hroð-
Etsy back up.
https://www.etsy.com/shop/NorseWest
After forever the forge is back in action. Trying to find a trip to Denmark/Germany. no customs just what is on here is available for now. Not back to knives yet. Hammer arm is a bit rusty yet.

Skål.
Hröð-
Jul

My Jul Will be between 12/21 and 1/18 so Glædelig Jul again & godt nytår.
Frohe Weihnachten und ein glückliches Neues Jahr.
Hröð-
Who Are The Corded Ware People (Updated)
Today we will discuss the Corded Ware Culture and the people associated with it culturally .
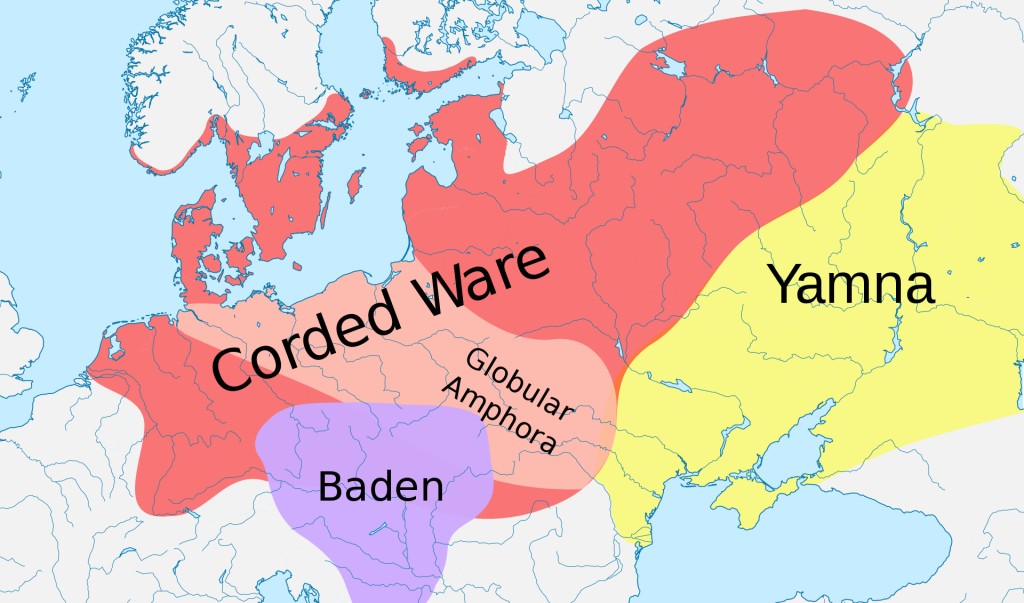
The Corded Ware culture is the western expression of the ancient Yamna or Yamnaya Culture of the Pontic/Caspian Steppes and possibly has components of West Central European Neolithic elements (David Anthony). Sintashta are the eastern expression of the Corded Ware and may represent what we today call Schythians, a mysterious Indo European tribe who seem to absorb or represent more than one later group. Genetically we see them connected with Gothic peoples, Slavs, Celts and some Uralic speakers as their empire stretched well across Eurasia. The Yamnaya people or maybe more accurately Proto Indo Europeans, theoretically appear to be the admixture of Caucasus Hunter Gatherers and Eastern Hunter Gatherers. R1B-R1A and G2A YDNA. The Neolithic farming communities of the Balkans and eventually all of Europe were descended from these Caucasus Hunter Gatherers as well (G2A). They had spread from the Caucasus into Anatolia and then to Europe. The Western Hunter Gatherer’s haplogroup ancestor (IJK) more than likely originated in the Caucasus or Iran. The I group then within Europe separated from IJK. R1B existed in Mesolithic Europe but rarely and did not see great expansion until the Corded Ware and Bell Beaker Complex. One of the Ancestral components of the Eastern Hunter Gatherer is the “Ancient North Eurasian” who is a common ancestor of Indo Europeans via the EHG and Siberian, Native American peoples via those who migrated to the Americas from East of the Urals. The Haplogroups U and H in MTDNA phylogenetic tree are children of the parent haplogroup MTDNA R. These represent a great deal of female European ancestry along with K, T and many others. The G haplogroup is technically a lesser branch of IJK from which the I, J and K YDNA groups are derived.
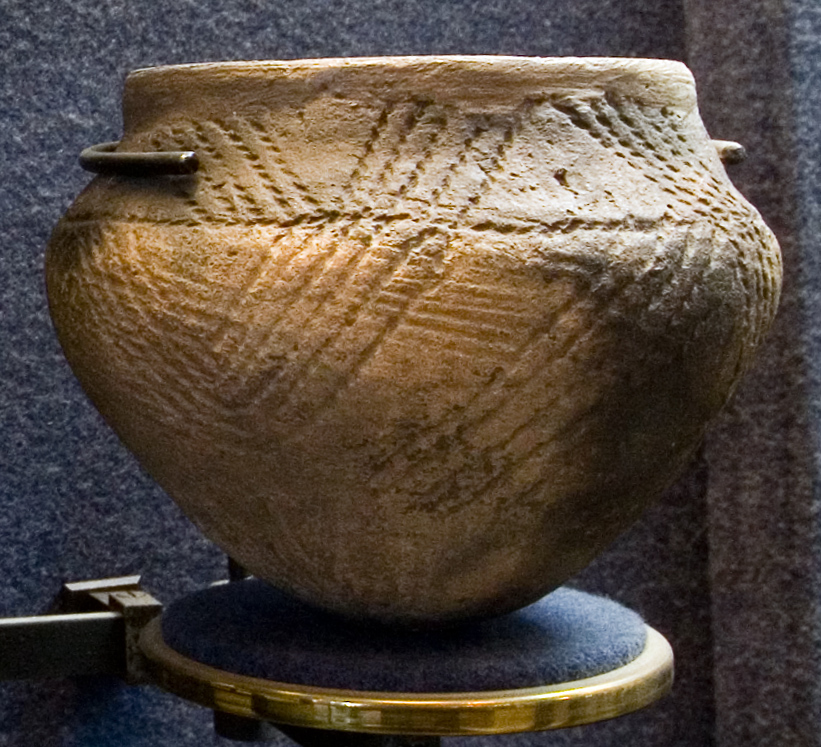
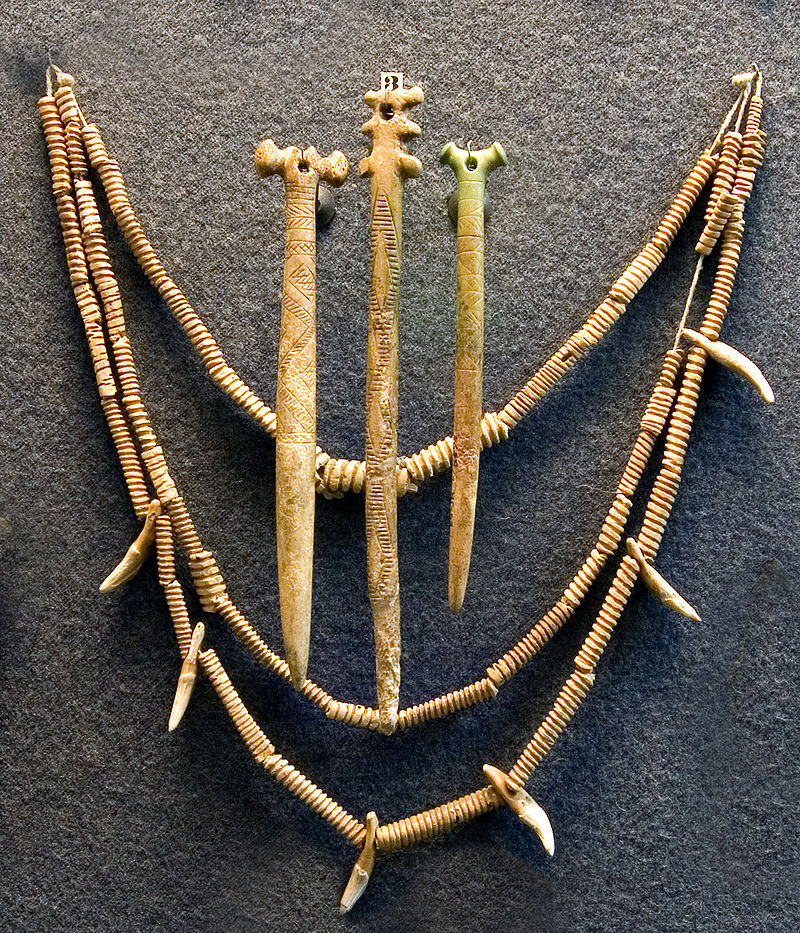









(Above) Yamnaya Culture related materials.
I DO NOT OWN THESE IMAGES , NORE DO I CLAIM ANY CREDIT TO THEIR CREATION. COPYRIGHT TO THE ORIGINAL CREATOR. MOST WERE TAKEN FROM WIKIPEDIA OR GOOGLE IMAGES.
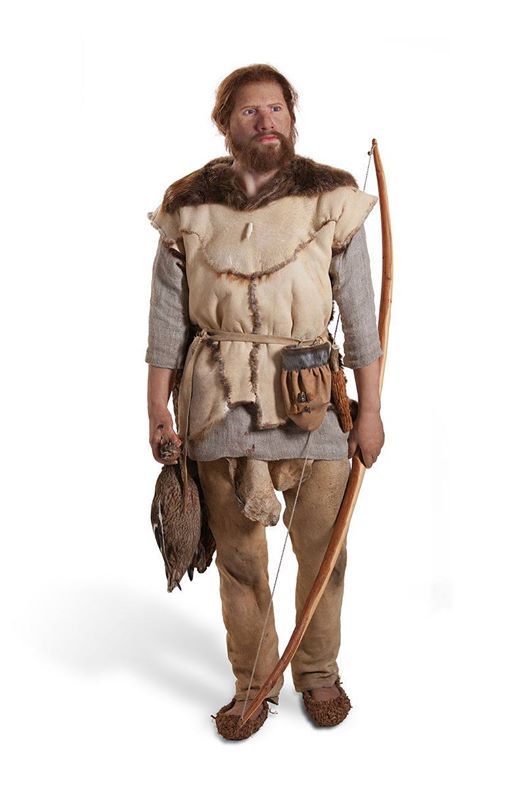
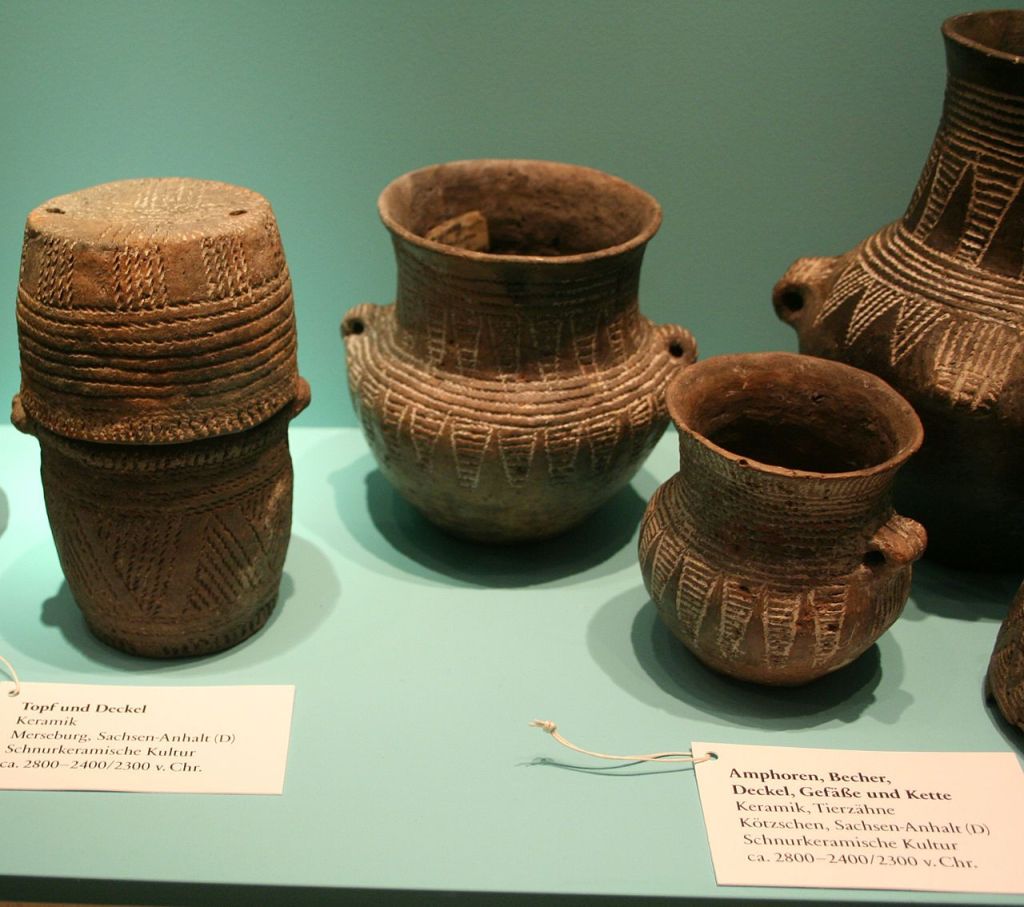









(Above) Corded Ware associated artifacts.
I DO NOT OWN THESE IMAGES , NORE DO I CLAIM ANY CREDIT TO THEIR CREATION. COPYRIGHT TO THE ORIGINAL CREATOR. MOST WERE TAKEN FROM WIKIPEDIA OR GOOGLE IMAGES.
The move from the Steppes to Central, Western and Northern Europe:

I DO NOT OWN THIS IMAGE: Source Google Search.
The people of Eurasia were largely Hunter Gatherers up till the Neolithic when groups in the Caucasus, Balkans and Anatolia began to develop and spread new farming technologies northward into Central Europe. In certain areas hunter forager cultures persisted such as in
Scandinavia and parts of the Urals and Western Steppe. Eventually Europe was overtaken by the new technologies and hunting centered life decreased but remained at least in some form as a guarantee against bad yields. The Farming groups represented by Varna, Vinca , LBK and others brought the Megalithic structures to western Europe and Scandinavia. It should be noted that signs of indigenous farming may have been detected before the arrival of Caucasian groups. These farming groups are believed to have been the evolution of the Caucasus Hunter Gatherer (CHG) a distinct group who’s G2A Haplogroup was the primary YDNA of the farming expansion while H in various forms and others were the MTDNA. The H groups also may have had some European distribution in the Mesolithic as well. The Northern contemporaries of the CHG were the Eastern Hunter Gatherer (EHG) centered in modern Russia, The Urals, Scandinavia and Finland. These Hunters were partly descended from the “North Asian Hunter Gatherer” and are the ancestral originators of the R YDNA group (R, R1B,R1A). It is suggested among other theories that the remaining CHG and EHG combined into a new culture and genetic group ancestral to the Yamnaya culture centered in Pontic Caspian steppes north of the Black Sea and Caucasus. This new culture with a complicated language began expanding in the late Neolithic north, South, East and West. The new culture was marked by changes in ideology, travel and customs demarcating them as different or novel from the previous farming and hunting cultures and separated from them by many generations. In a large picture they are the descendant in part from Farming groups but many generations removed. The language spoken was likely Proto Indo-European, a grammatically complicated heavily declined language resistant to barrowing from other languages. This language carried cultural terms unique to it revolving around horse domestication, wheels and mobile economy. It is theorized that this group was the first to tame and ride horses (Horse, Wheel and Language , David Anthony) and create a mobile semi nomadic wheel based economy. The oldest wheel to date on Earth was found in Slovenia at 5350 years old. This would place the wheel in the heartland of Neolithic European farming culture and at the edge of Expanding Steppe Cultures (PIE/WSH). It is also suggested (Theorized) that the Chariot was invented in the Steppes by PIE cultures and spread south via the Caucasus to the Middle and Near East. Archeology and linguistics supports this (David Anthony ). The remnants of words relating to these things are found throughout many ancient branches of PIE. The exact age of the branching is unknown, In David Anthony’s book he points out that Germanic/Baltic/Slavic might be the oldest branching after Anatolian and Tocharian . Also pointed out in David Anthony’s book the PIE language share deep relationships with Uralic language groups via very archaic shared pronouns and other features. In his book he relates the possibility of a shared Ancestor that by PIE and Uralic families descended from. Given the geography I think this is an interesting idea but these are now distinct language families and may have been related in only the most ancient sense. I would like to Add that the Basque language is sometimes referred to as a candidate for the only surviving Neolithic Language with no known membership in existing language families, however recent studies have found similarities with modern Caucasus based languages and the Basque share a similarity with Neolithic populations in a similar way as Sardinians. These Neolithic peoples were originally from the Caucasus and carried the Caucasian G2A Haplogroup that is prevalent still in the Caucasus and Mediterranean populations.
NOTE:
When I speak of interrelatedness to these ancient cultures it is through a modern lens and in no way reflects their actual interactions or relationships nor implies they saw themselves as related to each other.
Why the Expansion took place and what spurred it is unknown but archeology tells us that signs of steppe influence began to be detected in Late Neolithic cultures at the fringe steppe areas, Carpathian Basin, Danube Valley and other places. This included technology, status symbols and burial customs. Signs of hostile force is also detected where WSH groups replace or run out previous Neolithic cultures as they move west into Europe. Signs of peaceful coexistence also exist. The Western and Scandinavian hunters appear to have been most durable to this and you see the Hunter YDNA (I,I2,I1) persist in Scandinavia and have resurgence during the post Bell Beaker Central European Bronze Age. This however was not the case in Britain as the PIE DNA both Autosomaly and YDNA replaces the previous population within several generations. Britain is heavily WSH derived while Scandinavia retains as high as 60% Hunter derived YDNA (I1A) but via autosomal is heavily WSH derived. After 3000BC The Corded ware and their descendants start to become the majority culture in Northern Europe. The story in Southern Europe Is markedly different in that the culture existing when WSH people arrived were much more diverse.
It is believed the Corded Ware culture might have been the group responsible for introducing PIE languages to Northern Europe and other ascribe it as specifically Ancestral to Germanic culture however the Corded Ware horizon appears to be Ancestral all Northern European cultures including Germanic, Celtic, Slavic and Baltic etc. *My view is that the interaction with unique indigenous groups played at least some role in post CWC groups evolving into unique cultures we see today:
WEST CENTRAL EUROPE: Mesolithic to Later Iron Age.
+> indicates shared origin.
* indicates an adjacent culture and genetic contact with PIE groups.
These charts are not exhaustive to every culture or group.
Western Hunter Gatherer*
Neolithic Farmer*
CWC Horizon+>
Bell Beaker Trade Complex+>
Unetice+>
Tumulus+>
Urnfield culture+>
Hallstatt Bronze Age/Iron Age+>
Le Tene Culture (Iron Age)+>
Pan Celtic civilization +>.
NORTHERN EUROPE: (Mesolithic to Iron Age)
Western, Eastern and Scandinavian Hunters *
Neolithic Farmers*
Funnelbeaker Culture (Hunter/Farmer mixed) *
CWC+>
Single Grave Culture+>
Beaker Culture+>
Unetice Culture+>
Nordic Bronze Age+> (Recognizable signs of Germanic Culture)
Jastorf and Wielbark Cultures (Iron Age)+>
Pan Germanic Cultures+>
BRITAIN: Mesolithic to Iron Age..
Hunter Gatherer (First Population) *
Neolithic Farmer (Second population) *
Bell Beaker Chalcolithic Warrior (Pie)+>
Bronze Age Briton (Descended from Beaker)+>
Le Tene Celtic culture+> (Arrives from NW Europe Iron Age)
British Celtic Tribes+>
EASTERN EUROPE:
Eastern Hunter and North Eurasian Hunter+> (Ancestor to Sredny-Stog-Yemnaya)
Western Hunters+>*
Caucasus Hunter+>*
Neolithic Farmers+> CHG* (Simplified term for many cultures)
Contemporary Forager Cultures *
Sredny Stog (Pre PIE? EHG-CHG) +>
Yamnaya (Pie) +> (EHG and CHG)
Corded Ware-Fatyanovo, Sintashta, Andronovo, Srubnaya Etc.+>
Únětice culture+>
Lusation Urnfield Culture +>
Schythians and Aryans (Non political meaning)+>
Pre Slavs?+>
This is just to give a bare idea of the influence of Steppe culture throughout Europe.
Tumulus and Urnfield cultures are mentioned as possibly Ancestral to Celtic culture which was later expressed by the Hallstatt Culture. Often Germanic and Celtic are placed close in the PIE family tree but recent opinions have linked Italic and Celtic as a western branch and Germanic, Baltic and Slavic as a Northern Branch. This being said it is not hard to see a general relatedness especially in the ancient form of each of these languages. Their exact correct placement is unknown as is their exact date of branching. Germanic may have branched as far back as 3500BC or as recently as the Nordic Bronze Age. Germanic customs have a certain amount of unique traits that may be remaining elements of the Pitted Ware Culture or other Scandinavian Hunting groups. As mentioned above Germanic populations are generally higher in Hunter and then Steppe ancestry while southern Europe is more farmer derived. Central Europe being the epicenter of WSH culture (PIE) has high relations rates to Yamnaya derived groups with less hunter and farmer. South Eastern Europe also has distribution WHG I2A. Neolithic female populations play a greater role in Northern Europe than male lineages as G2A is rare but I-M170 with its descendants and R1B/R1A are frequent. Germanic culture appears at least with current information to have been born out of the Hunter/Corded Ware and Single Grave/Bell Beaker group in Jutland or Southern Sweden. It then developed into the Nordic Bronze Age with at least some influence from Unetice and Hallstatt via trade and other contact. All of this of course is hypothetical postulating.
A further note:
In the ideas above I have simplified many elements and the info is not exhaustive. I also want to make sure that the Neolithic cultures are not under represented. The Funnelbeaker Neolithic culture was very widespread in Scandinavia and butted up to remaining Scandinavian hunters like the Pitted Ware culture. This same culture (Funnelbeaker) was also in Germany, Poland and Czechia when the Late Yamnaya arrived from Eastern Europe/Western Steppes. David Anthony proposes they arrived through the Danube Valley and that Corded Ware was a local construction that the Yamnaya made contact with and this grew into the wide spread Corded Ware culture that may have brought PIE languages to Northern Europe. They may have also carried not just PIE elements but remaining Neolithic elements as well. He also proposes the Beaker folk was a pre existing culture that Corded Ware made contact with but we know now via DNA that the Beaker Culture was descended from the same source population as Corded Ware and Yamnaya. In the Same section of his book it is put forth that the Ancestor of Germanic bifurcated from PIE in Eastern Europe which may be true but the actual language we know as Germanic I personally believe developed in Scandinavia nor central Europe during the Corded Ware/Single Grave period . On the subject of Bell Beaker I want to touch on my previous articles and after gaining further insight from the second time I read The Horse, Wheel and Language. The Bell Beaker designs appear to be either evolution from Corded Ware or Funnelbeaker/Corded/Protruding Foot Beaker designs or cruder copies of a Neolithic Iberian design. The Atlantic EBA was flourishing at this point and these could have been traded north from existing Neolithic crafters into arisen Yamnaya descended areas. We know via DNA the Beaker folk were not local to Western Europe but part of migratory Steppe peoples who likely Spoke PIE languages. It could be seen in a way that the Bell Beaker people (not pottery) were just the western most expression of Corded ware that picked up a new pottery style. Other Proto Indo Europeans groups earlier in development sometimes used pottery from surrounding areas. Sintashta and other CWC derived groups became unique eastern branches of CWC so why not a western most branch? The basic traditions of Corded Ware/Battle Axe/ Single Grave were intact in the Bell Beaker horizon. These traditions included single grave burials with goods like stone axes or hammers, copper daggers and Kurgans erected above the grave. The Beaker People represent the majority of British ancestors but are we to believe CWC just stopped at the coast and Beaker people had no connection?. We now have DNA to answer the question that yes The Beaker Folk were Corded Ware and that R1B was prevalent in CWC peoples. Some make them ancestral to Germanic, some to Celtic and Italic cultures. I would also like to add that I agree with the theory that Germanic, Baltic and Slavic belong in a branch together and Celtic and Italic belong in another branch around the Alps perhaps. If you look at word forms and etymology Celtic and Italic languages share some traits as well and mythology elements. If you look at certain words and mythology between Germanic, Baltic and Slavic languages certain elements are shared such as a female personification of the Sun, symbols, cosmology and animistic nature worship elements. A great deal of shared elements can be seen across Indo European religion and Germanic and Celtic people had considerable contact with each other but so did Germanic, Baltic and Slavic peoples. The contribution of the stone axe in the Corded Ware/Battle Axe cultures may have been pre-existing among the Funnelbeaker and other Indigenous groups. The Neolithic cultures of Europe, although likely distributed via Female lineages should not be underestimated either. It is recorded that males in the LBK culture of Central Europe’s Neolithic were buried with Stone axes. These males made little impact genetically but their women and traditions may have.
I hope this inspired you to dive into European Anthropology. Please go read and make up your own mind. I am only an amateur but find it endlessly fascinating.
Books and resources:
The Horse, The Wheel and Language by David Anthony (Highly detailed)
Skelhøj by Madz Kähler and Marrianne Rasmussen (Very Technical)
Bronze Age Metal Work by Nørgaard (Very Technical)
The Mound People by Glob
The Bog People By Glob
Myths and symbols in Pagan Europe by H.R Ellis Davidson (Early Celt and Germanic religion)
Eupedia.com (Great Maps and info on DNA)
Wikipedia.com (with a grain of salt/check other sources)
Wiktionary.com (etymology and tables)
Youtube.com (Good Documentaries)
Happy researching!!
Hroð-
Gruß Vom Krampus (belated)

Krampusnacht
Hroð-
Anglo Saxon grammar ideas
Anglo Saxon grammatical ideas and dative in semi poetic use:
The AS language retains the archaic Indo-European function of cases and gender as well as complicated poetic grammar that uses cases to imply words that are not actually written. In modern Germanic language only German and Icelandic retain cases and gender in any heavy use. Swedish and Danish have Common and Neuter in modern use. Danish and Old English share sometimes a visually close vocabulary but many are false friends and mean something different. AS uses cases not word order to indicate grammar and is more free in word order. This does not mean it is totally free or random in word order.
(The genders are meaningless in function in AS and only serve as a complicated archaic hold over from Proto Germanic and act as another layer of things to memorize. My interpretation from “Robert E Diamond” Old English grammar/ reader).
The following is my own writing of what I have learned.
The dative:
“Hail to the Sun”
The sun is receiving the call so it is singular dative.
I am the one hailing so I am in nominative.
Hælu Þære Sunnan (hail the sun) “to” is implied when using the dative and technically so is “the” so you could write it “Hælu Sunnan” and “ to the” ís implied and would be understood as such. The ending “an” on the Goddess name Sunne denotes a weak declension of the feminine noun. “Þære” ís the feminine dative form of “the” the nominative (f) form of the is “Seo”. Male Form(n) “Se” which is close to PG and PIE sources.
To add a personal emphasis I could add “Ic”
“Ic Hælu Þære Sunnan”
“I hail the sun”
As you can see Ic is cognate to German Ich.
When using articles (words like “the”) the article must match the gender of the word and the articles case must match the case being used. Dative with dative etc…
Example: masculine:
Se (nom) Hund (nom)
“The Dog” the dog is the subject so it is nominative as is “the”
Se Hundas (Nom/Plural)
“The dogs” plural
Þæs Hundes bān (Genitive)
“The dog’s bone”
(Accusative uses the same word endings as nominative) but uses several different articles depending on gender such as “þone”. The ACC case is used to denote the object being given such as above “bān”. In the modern sentence “I gave the dog a treat” the “treat” is accusative the dog is singular dative. The accusative is also used to indicate movement of something in a sentence such as running, riding, charging etc..
The dative case has the most uses and is the most complicated.
Dative:
“To the Hall” as in a toast
Sæle (neut) (tó the hall) poetic
“To the halls” “ (of our forebears) plural toast
Sælum (neut) dative plural “ to the” ís implied.
Sæl is the origin of the Word Saloon and Salon. Modern Danish “Sal” as in Mjødsal (Mead hall) Old English “Medusæl”
All cases and genders have a version of the word “the” and some are shared. Cases have some of the following endings: ( not complete or exhaustive)
E
A
es
as
U
an
Some case endings on certain words have no end vowel or sometimes use a double from another such as sometimes genitive ending E or Nominative ending in A.
This level of complexity leaves the student with need of complex tables showing all gender forms, articles by case and gender as well as all singular and plural forms of words. Wiktionary and and a good word hoard book goes a long way.
Notes:
Anglo Saxon is a Norð Sea Germamic or Ingveonic language that originated in Jutland and Southern Scandinavia. Old English, English, Old Saxon, Low German, Old Frisian and Frisian are all within the Ingveonic family. Some speculate the Teutons were also Ingveonic due to their southern Scandinavian origin. These languages sit somewhere between Scandinavian and West Germanic languages.
I use Peter S. Baker, Robert E Diamond and Stephen Pollington, K Herbert resources as well Thijs Porck videos and wiktionary declension tables.
Skål 🍻 some of this might not correct but it’s as far as I have gotten.
Hroð-
Wow

Sometimes you should visit old bookstores. You Never know. full 1907 set royal edition 57 of 450.
Hroð-
Anglo Saxon word of the day: Yþlad
Anglo Saxon word of the day:
ȳþlād (voyage, crossing) poetic sense.
From:
Proto-West Germanic: *unþi
Old English: ȳþ
Middle English: ythe, uthe, ithe
English: ithe
Old Saxon: ūthia
Old Dutch: *unthia, *untha
Middle Dutch: unde, onde
Dutch: onde (dialectal)
Old High German: undia
Middle High German: unde, ünde
German: Unde (obsolete, dialectal)
Yiddish: אינד (ind)
Old Norse: unnr, uðr
Icelandic: unnur
And:
Old English: lād, ġelād
Middle English: lad, lode, loode
Scots: laid, lade
English: lode, load
Old Frisian: lāde, lēde
Old Saxon: lēda
Middle Low German: leide
→ Norwegian: leide
→ Old Swedish: leidh
Swedish: lejd
Old Dutch: *lēda, *leida
Middle Dutch: leide
Dutch: lei
Old High German: leida
Middle High German: leite, geleite
German: Leite, Geleite
Old Norse: leið
Icelandic: leið
Faroese: leið
Norwegian:
Norwegian Bokmål: lei, led
Norwegian Nynorsk: lei
Old Swedish: lēþ
Swedish: led
Danish: led
→ Proto-Finnic: *laita
Estonian: laid
Finnish: laita
→ Proto-Samic: *lājδ
Bonus:
Wrǣtt (Ornament, jewel)
Hroð-
Anglo Saxon word of the day: acweorna
Anglo Saxon word of the day:
ācweorna (squirrel)
The first denotes “oak” the second element “weorna “ denotes squirrel.
Proto-West Germanic: *aikwernō
Old English: ācweorna
Middle English: acquerne
Old Frisian: *ēkworna, *ēkhorna
Saterland Frisian: *Eeker (in Kateeker ?)
West Frisian: iikhoarn, iikhoarntsje
Old Saxon: *ēkhorno
Middle Low German: êkhōrn, êkhōrne, eikhōrne, êkhorn, êkōrn, eikōrn, êkōrne, echhorne
⇒ Dutch Low Saxon: Eekhoorntje
German Low German: Ekkern
Westphalian:
Ravensbergisch: Aik, Aikern
Sauerländisch: Ēksken, Aikerte
⇒ German Low German: Eekhoorntje
Old Dutch: *ēcorno
Middle Dutch: êencōren
Dutch: eekhoorn
Old High German: eihhorno, eihhurno
Middle High German: eichurne
Alemannic German: Eichhore
German: Eichhorn
⇒ German: Eichhörnchen
⇒ Hunsrik: Eichhernche
Old Norse: íkorni
Icelandic: íkorni
Faroese: íkorni
Norwegian:
Norwegian Bokmål: ekorn
Norwegian Nynorsk: ekorn, ikorn
Old Swedish: ēkorne, īkorne
Swedish: ekorre, (dialectal) ikorn
Old Danish: īkærnæ
Danish: egern
Westrobothnian: ickȯrn, ikårn, ikkårn
Elfdalian: aikuonn
Jamtish: íkuðn
Gutnish: eikånn
Scanian: igarne
Bonus:
maniġfeald (manifold, many fold, of many parts)
Old English: maniġfeald, mæniġfeald
Middle English: manifald, monifald, manyfold, manifold
English: manifold, manyfold
Old Frisian: manichfald
Old Saxon: managfald
Old Dutch: *manigfald
Middle Dutch: menichvout
Dutch: menigvoud, menigvoudig
Old High German: manicfalt, manicfaltīg
Middle High German: manecvalt, manecvaltec
German: mannigfaltig
Old Norse: margfaldr
Icelandic: margfaldur
Norwegian: mangfoldig
Old Swedish: mangfalder
Swedish: mångfald, mångfaldig
Danish: mangefold
Gutnish: manggfaldur
Gothic: 𐌼𐌰𐌽𐌰𐌲𐍆𐌰𐌻𐌸𐍃 (managfalþs)
Hröð-
Anglo Saxon word of the day: Geryne
Anglo Saxon Word Of the day:
ġerȳne (mystery) using the word “Run” (rune)
Proto Germanic “garūniją”.
Proto-West Germanic: *garūnī
Old English: ġerȳne
Middle English: irīne, *yrīne, ʒerīnu (pl.)
Old High German: *girūni
Middle High German: gerūne, geriune
German: Geraune
Gothic: 𐌲𐌰𐍂𐌿𐌽𐌹 (garūni)
Bonus:
ċeahhettan ( to laugh loudly, cackle)
Hroð-
Anglo Saxon word of the day: Preowthwil
Anglo Saxon word of the day:
prēowthwīl (to blink) (the time it takes to blink)
Bonus 1:
Hagosteald (an unmarried warrior of royal descent) (bachelor)( liegeman) (owner or one who lives on fenced land of their family) sometimes acts as a personal name. Alternate:Hægsteald.
Old English: hæġsteald, hagulstead, hagosteald
⇒ Old English: Hagustealdesēa
⇒ Old English: Hagustealdeshām
English: Hexham
Middle English: hassel, haselle
Old Saxon: hagalstad
Old High German: hagalstalt, hagastolt
Old Norse: haukstalda
Bonus 2:
wīġbǣre (warlike) (eager for battle)
Hroð-
Anglo Saxon word of the day: Scytta.
Anglo Saxon word of þe dæg:
Sċytta (archer, shooter, Sagittarius)
Bonus:
Sċēotan ( to shoot, fire, the act of shooting, quick movement, to rush, to dash)
Proto-West Germanic: *skeutan
Old English: sċēotan
Middle English: shoten
English: shoot, skeet
Scots: schute, schuit, schote, schoot, schete
Old Frisian: skiata
West Frisian: sjitte
Old Saxon: skiotan
Middle Low German: scheten
Low German: scheten
Old Dutch: skietan
Middle Dutch: schieten
Dutch: schieten
Limburgish: sjete
Old High German: sciozzan
Middle High German: schiezzen
Alemannic German: schieße
Central Franconian: schieße, scheeße
German: schießen
Luxembourgish: schéissen
Vilamovian: śisa
Old Norse: skjóta
Icelandic: skjóta
Faroese: skjóta
Old Swedish: skiūta
Swedish: skjuta
Norwegian Nynorsk: skyte, skyta, skjota (archaic)
Old Danish: skiūtæ
Danish: skyde
→ Norwegian Bokmål: skyte
Westrobothnian: skjuut
Elfdalian: stjuota
Jamtish: skjǿte
Old Gutnish: skiauta
Gutnish: skjaute, skiauta
Scanian: skjúda, skúda
Crimean Gothic: schieten
Anglo Saxon word of the day: Tirgan.
Anglo Saxon word of þe dæg:
Tirġan (ᛏᛁᚱᚷᚨᚾ) ( to provoke, pain, irritate)
Old English: tergan, tiergan, tyrgan, tirgan, tirian; tierwan
Middle English: terien, tarien, taryen; terȝen
Scots: tarrow
English: tarry
Old Frisian: *tergia
West Frisian: tergje
Old Saxon: *targian, *tergian
Middle Low German: tergen, targen
→ Danish: tærge
→ Norwegian: terge
→ Swedish: targa
Old Dutch: *tergen
Middle Dutch: tergen, terghen
Dutch: tergen
Old High German: *zergen
Middle High German: zergen
German: zergen
Bonus:
Torht ( to shine, brightness)
Old English: torht
Middle English: torhte, tohte
Old Saxon: torht, toroht
Old High German: zorht, zoraht, zorft
Hroð-
Anglo Saxon word of the day: Uhta
Anglo Saxon word of þe dæg:
ūhta (pre dawn) (last part of night)
Old English: ūht (< *unhtwaz), ūhta (< *unhtwô)
Middle English: *uht (found in compound uhtsang, uhtsong); Middle English: uhhtenn, uȝten, ughten, oughten (< Old English ūhtan, oblique form)
Old Saxon: ūhta
Middle Low German: uchte
German Low German: Uchte, Ucht
→ German: Uchte (“midnight mass”) (regional)
Old Dutch: *ūhto
Middle Dutch: uchte, ochte (various forms are attested, including nuchte through rebracketing, uchten/ochten from the case forms, and rarely uchtent/ochtent from the previous by analogy with avont (“evening”))
Dutch: ochtend
Old High German: uohta (irregular); *ūhta
Middle High German: uohte, ūhte (both rare)
German: Ucht, Aucht (both only in placenames and compounds)
Old Norse: ótta
Icelandic: ótta
Norwegian Bokmål: otte
Westrobothnian: ótt’
Old Swedish: ōtta, ōta
Swedish: otte, otta
Danish: otte
Gothic: 𐌿𐌷𐍄𐍅𐍉 (ūhtwō)
Bonus:
Lagustrǣt (ocean) literally “Water-road”.
Old English: strǣt, strēt
Middle English: strete, streete, stret, strate, street, stræt
English: street
Scots: street, streit, stret
→ Breton: straed
→ Cornish: stret
→ Welsh: stryd
→ Old Irish: sráit (see there for further descendants)
→ Old Norse: stræti (see there for further descendants)
Old Frisian: strēte
North Frisian:
Föhr-Amrum: struat
Mooring: stroote
Saterland Frisian: Sträite
West Frisian: strjitte
Old Saxon: strāta
Middle Low German: strâte
German Low German: Straat, Stroot
Old Dutch: strāta
Middle Dutch: strâte
Dutch: straat (see there for further descendants)
Limburgish: sjtraot, straot
Old High German: strāza
Middle High German: strāze
Alemannic German:
Swabian: Schdrôs
Bavarian: Stråßn, Strossn
Apeltonerisch: Streoss
Mòcheno: stros
Upper Bavarian: Straß
Central Franconian: Stroß
Eifel: Strooß
Hunsrik: Stros
Luxembourgish: Strooss
German: Straße
Rhine Franconian: Schdrooß
And
West Germanic: *lagu
Old English: lagu, lago
Middle English: laȝe, lawe, laie, leye
English: lay
Old Saxon: lagu
Old Norse: lǫgr
Icelandic: lögur
Faroese: løgur
Norwegian Nynorsk: log
Norwegian Bokmål: låg
Old Swedish: lagher
Swedish: lag
Old Danish: low, lou
→ Scots: lyog
Gothic: *𐌻𐌰𐌲𐌿𐍃 (*lagus) (> 𐌻𐌰𐌰𐌶 (laaz))
Hroð-
Book of the month (June)

Hilda Roderick Ellis Davidson is quickly becoming a favorite author of mine. Great detail and everything kept in context. I do love comparatives though I am biased.
Hrøð-
Yule-Ġēol-Jul (hāliġdæg)

(Public Domain)
Anglo-Saxon-Norse reference:
þ Th-(Th)or “Thorn”
ð Th-Wi(th) “Eth”
The Yultide is a custom or holiday from Germanic culture predating the suppression and removal of native European customs by the church. The month begins at “ǣrra ġēola” Yule is a season/month of the year. Most of the customs associated with modern day Christmas are lifted from Germanic and Celtic traditions. The Tannenbaum stems from early modern era Germany however the custom of evergreens as symbols of immortality in dark winter times goes well back to our Ancient past, possibly even as far back as the hunters and farmers. It should be noted the evergreen decorations were widely used across the world in indigenous polytheistic religions. The word Yule comes from Anglo Saxon Ġēol (G says Y) and is believed to have derived from PIE word meaning joy, however I have found etymology suggested it is related to a word meaning wheel as in the cycle of seasons or Sun. In Nordic countries the word still stands for anything related to Christmas or Yule in the form “Jul”. Yuletide meaning the “Yule-Time” referring to the period of Yule. In Anglo Saxon there is “ǣrra ġēola” (Before Yule) and “æfter ġēola” (After Yule). One of Odin’s names is Jolfaðr (Yule Father). This period is also known as Midwinter. In the Anglo Saxon seasons October 31st is Winterfylleð thus making ġēol Midwinter. Many customs representing various aspects of lore like Santa Clause comes from a mixing of stories and traditions. The Jolfaðr gift giver likely derives from Odin but the Greek Saint Nicholas had its influences and various traditions began to merge across Europe. Characters like Krampus, The Tomtens, Elves and more are derived from Pre Christian traditions of the Midwinter. We also see in Sweden the Julbocken (Yule Goat) in Sweden. These Goats draw a carriage with the Tomten aboard carrying gifts. Many traditions in the Alps have Krampus or other Woodwose like creatures who travel with A Jolfaðr like figure dishing out whippings on naughty children. Also Young men dress as creatures and chase young women, a custom likely primordial in nature. The Baltic Countries have similar traditions as well as Slavic regions. Some of these traditions likely passed down to us from the Alpine Celtic tribes. It pervades Indo European culture even after the suppression of our native religions. What we have in America or other western English speaking areas is a spattering of all the traditions brought by our ancestors from Germany, Poland, Scandinavia, Holland, England etc. In reality it is a beautiful and positive Holiday centered around feasting, folk legends, ancient cultural customs and a sense of joy or merriment in the dark half of the year. Those in the Northern hemisphere have a period that is long and drawn out till spring. The prospect of good fun, feasting, mead and rituals to keep kin safe and in prosperity brought hope to our ancestors in the dark winter. Had they not persisted where would we be?
The Wild Hunt:

The Wild Hunt or Wild Host is a mythological event from the deep past believed to be taking place between Between Winterfylleð and ġēol. Customs from Germany, England, Scandinavia and The Alps all depict some form of this ghostly procession. Each depiction lends a local flavor to the cycle but the central theme is Ancient Gods and hunter spirits drive horses and hounds across the night sky in a great booming host. Most well known perhaps is that Oðinn/Woden/Wotan leads this host and has returned to Middangeard to collect the lost souls wandering the Earth. Other stories have þorr leading or Frigga in the form Frau Wode (Wodan’s wife). I have a very deep ancestral connection to this particular folk story in Mecklenburg and Uckermark North Eastern Germany. Frau Wode or Frekka leads the host and brings either misfortune or good fortune depending certain circumstances, she is also followed by a pack of hounds with glowing eyes who can wrought serious damage. Other tales have her simply assisting while Wodan leads though It should be noted that this Goddess or Form of Frau Frekka/Frick is deeply entrenched in the folk legends of North Eastern Germany. In England local versions exist with unique local Deities or spirits wandering the winter nights with packs of hunters and hounds such as Herne the Hunter. The concept of the Wild Hunt could derive from Celtic roots or be equally shared amongst Germanic and Celtic peoples of antiquity. The concept of the Wild Hunt follows the basic native European view that Samhain or Winterfylleð (Among other names) is the opening of the energetic spiritual veil where these mystical beings enter our reality to do any number of tasks on Earð. Frau Wode would as described above be accompanied by hounds who may slip into your home to warm itself by the fire. If you attempted to remove the hound it would turn to stone and return to life every night at midnight to howl. Each howl was a curse on the family of the offender. Only Frau Wode can break the spell on Christmas eve. I associate the Goddess Frau Wode with Frigga given a decent amount of etymological/linguistic evidence.
Tannenbaum:

Glade Jul by Viggo Johansen (Danish Painter)
We know the basic modern Tradition of the Tree is from Germany and was introduced elsewhere by Germans however we do not know how deep the tradition stems back to pre christian times. Germanic tribes worshipped trees and had the Sacred Yggdrasil and Irminsul. The bringing in of Greenery in the winter is ancient in origin and possibly associated with a Yule-Tree like concept but evergreens as stated above were used across the world. As with many of the discussed traditions it is now merged with other later traditions. I personally view the Tannenbaum as a symbol of life in dark cold times and that sentiment is repeated in the book “The Solstice Evergreen” by Sharyl Karas (1991) that covers the use of Evergreens in several cultures.
A unique tradition among Shetlanders (Scotland). Article link bellow.

Photo is from Scotsman.com
Krampus:

Krampus who has risen to modern popularity is arguably a hold over of much earlier Native European customs amongst Alpine Celts and Germanic tribes who was easily applied to later traditions. We see this custom of dark and light play a roll in the Winter Solstice across Europe. the Dark and sinister yet humorous Krampus and the Jolly wise gift bringer. This combined with ancient beliefs in the Woodwose, Ettins, Elves , Wild men and Gnomes bring these beings front and center for the Yule Tide festivities. We see similar characters across Europe in similar but unique customs to their regions. The magic of snowfall over mountains and the whisping presence of Wotan’s host as the beings of ancient lore visit for a Glühwein or Gløgg. Best be a good host or Krampus might cut a switch. Bruce, Mourice (1958) writes that no other figure could Krampus reflect than the Horned God of Ancient Europe. Depictions of the Celtic God Cernunnos show him fully adorned in Antler headdress in a meditative state.

Credit: National Museum of Denmark. Natmus.dk. Gundestrup Cauldron.
Tomten or Nisse:

Credit: Nasjonalbiblioteket Norway.
The Nisse (Danish/Norwegian) and Tomten (Swedish) is a small (but sometimes 2ft t) house spirit in Scandinavia who looks like the popular depiction of Gnomes. These generous fellows help out with the farm or house and keep prosperity or good luck for the property. The Book (The Tomten) by Astrid Lindgren based on poems by Viktor Rydbergand Karl-Erik Forsslund is one of my all time favorite Holiday stories and is available on Audible (Not sponsored). The collecting and decoration of Tomtens is now very popular and has become popular outside of Scandinavia. Should you fail to give the Nisse his due (a special porridge) and the butter be misplaced he may exact revenge on you or your property. In modern Sweden he is the gift giving character.

John Bauer (1912) Julbocken.
Jolfaðr-Ġēolfæder:

(Photo Copyright unknown)
There is a myriad of articles about the nuance that led to Santa Clause so I will leave that be. I will however talk about Oðinn as Santa Clause. The old wise one eyed God was known also as Jolfaðr (Yule Father) or Jolnir (Yule one) and he brought gifts but the Reindeer were nowhere to be found. He rode across the sky upon his horse Sleipnir. The tradition of hanging stockings originates hear from my research as carrots were left out for Sleipnir to eat. Oðinn also is one of many figures associated with the Wild Hunt where he rides and claims lost souls from Winterfylleð to Ġēol. Oðinn is among the most multi faceted Gods in that he is both a grim and stern God of death, battle, honor and war but also a God of wisdom, poetry, ecstasy, mirth, victory (Sig) and feasting.

Georg von Rosen – Oden som vandringsman, 1886 (Odin, the Wanderer.
Yule Lads (Iceland):
The Yule Lads are a fairly modern (17th century) Holiday custom in Iceland where 13 Yule lads come to town and cause havoc if not given their favorite snacks. If given their snack a gift will be left in a shoe n the window sill. Some of the terminology is older like their Mother Gryla who appears as a Troll in older stories.
https://icelandwithaview.com/the-13-yule-lads-of-iceland/
Yule Log:
1725 Henry Bourne suggests:
Our Fore-Fathers, when the common Devices of Eve were over, and Night was come on, were wont to light up Candles of an uncommon Size, which were called Christmas-Candles, and to lay a Log of Wood upon the Fire, which they termed a Yule-Clog, or Christmas-Block. These were to Illuminate the House, and turn the Night into Day; which custom, in some Measure, is still kept up in the Northern Parts. It hath, in all probability, been derived from the Saxons. For Bede tells us, That [sic] this very Night was observed in this Land before, by the Heathen Saxons. They began, says he, their Year on the Eight of the Calenders of January, which is now our Christmas Party: And the very Night before, which is now Holy to us, was by them called Mædrenack, or the Night of the Mothers … The Yule-Clog therefore hath probably been a Part of those Ceremonies which were perform’d that Night’s Ceremonies. It seems to have been used, as an Emblem of the return of the Sun, and the lengthening of the Days. For as both December and January were called Guili or Yule, upon Account of the Sun’s Returning, and the Increase of the Days; so, I am apt to believe, the Log has had the Name of the Yule-Log, from its being burnt as an Emblem of the returning Sun, and the Increase of its Light and Heat. This was probably the Reason of the custom among the Heathen Saxons; but I cannot think the Observation of it was continued for the same Reason, after Christianity was embraced.
(Wikipedia)
The Date:
The overwhelming accepted date of Yule is on the Winter Solstice (12/21/12/22) . This being said some scholars have suggested dates such 1/28 based on theories around a lunar calendar. The Mōdraniht of the Anglo Saxons was set at what is now Christmas Eve as attested by Bede but in January (See above) A Night/Ritual/Holiday celebrating female ancestors. This may have been related to fertility ritual aspect at Yule-Tide. The exact date can be described as up for debate but currently most hold events on or around the currant Solstice dates. It should be noted that both January and December held the name Ġēol and the calendar did not match what we have today which has led to debate and theories on the exact debate.
Yule belongs to all of us who’s ancestors contributed to it over thousands of years. It has changed as all things do. some deny its origins, others embrace the ancient past while others see it as something secular however factually inaccurate that might be. Thankfully we live in a time and place where if we disagree on such details the worst it might end up is a dirty look or argument. Yule is an inspiring time of year for us not unlike it was for our ancestors. Never fear to dig deeper into the past for it is full of wisdom from our forefathers. These posts are just small samples of the folklore from Northern Europe. Take a stroll on Yule at midnight and see if you can hear the distant cry of hunters or Wodan calling his wayward souls.

(Public Domain)
Glæd Ġēol
Hroðbeorht-
Celto-Germanic Book List (Non fiction)
Here is a few recommendations of books I have enjoyed over the years or am currently reading.
(I am not responsible for antiquated views or pseudo history in these books but I believe they still may contain interesting information or images)
)))))))Some books may be difficult to find(((((((
The Early Germans By Malcolm Todd.
Rise of the Celts by Henry Hubert.
The Goths by Peter Heather.
Norsemen of the Viking age by Christiansen
The Anglo Saxon Mead Hall by Stephen Pollington.
Aspects of Anglo Saxon Magic by Bill Griffith.
The German Folklore Handbook by James R. Dow.
Hallstatt 7000 by Kern/Lammerhuber.
Bronze age Metal work by Heide W. Nørgaard
Time life books The Celts: Europe’s people of Iron.
The Mound People by P.V. Glob
The Bog People by P.V. Glob
The Celts: Conquerers of Europe by Mohen/Eluere (Abrams Discoveries series)
The Bronze Age in Europe by Eluere (Abrams discoveries series)
The Pictish Guide by Elizabeth Sutherland.
All Osprey “warrior” illustrated books on Norther Europe.
The Northern World by Abrams Publishing.
Stephen Pollingtons wordcraft Old English dictionary.
Old English Grammar/Reader by Robert E. Diamond.
Introduction to Old English BY Peter S. Baker.
The World Guide to Gnomes, Fairies, Elves, And Other Little People by Thomas Keightley.
Norwegian Troll Tales by Joanne Asala.
Swedish Folk Tales and Legend by Blecher/Blecher.
Scandinavian Folk Belief and Legend by Kvideland/Sehmsdorfs.
Th Vikings by Else Roesdahl.
Looking for the lost Gods of England by Kathleen Herbert.
Hippocrene Beginner Language books with Audio Cd’s.
The Complete Grimms Fairy Tales by The Brothers Grimm.
Teutonic Mythology by Jacob Grimm.
Elves Wights and Trolls by Kveldulf Gundarsson.

Photo from the web. Credit unknown.
Enjoy!
Hroðbeorht-
Žaltys of Saule

Large Snake charm inspired by Žaltys of Saule. The Grass snake in Baltic mythology is a sacred animal of the Sun Goddess Saule. Forged iron.
Hroðbeorht-
Alpendahl Forge.















