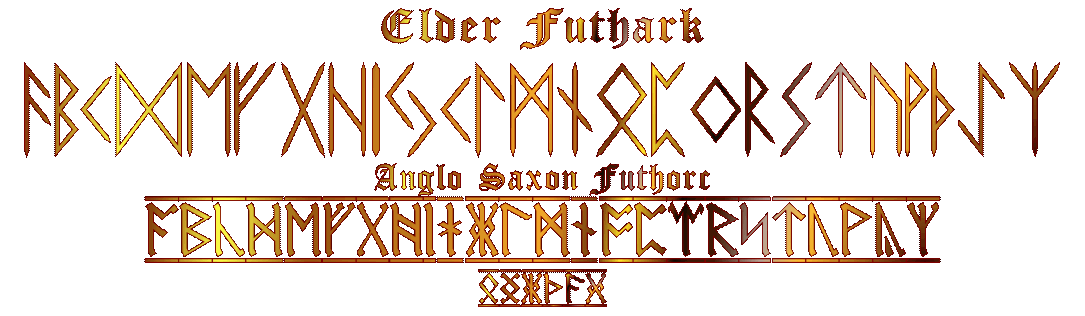Anglo Saxon word of the day: acweorna
Anglo Saxon word of the day:
ācweorna (squirrel)
The first denotes “oak” the second element “weorna “ denotes squirrel.
Proto-West Germanic: *aikwernō
Old English: ācweorna
Middle English: acquerne
Old Frisian: *ēkworna, *ēkhorna
Saterland Frisian: *Eeker (in Kateeker ?)
West Frisian: iikhoarn, iikhoarntsje
Old Saxon: *ēkhorno
Middle Low German: êkhōrn, êkhōrne, eikhōrne, êkhorn, êkōrn, eikōrn, êkōrne, echhorne
⇒ Dutch Low Saxon: Eekhoorntje
German Low German: Ekkern
Westphalian:
Ravensbergisch: Aik, Aikern
Sauerländisch: Ēksken, Aikerte
⇒ German Low German: Eekhoorntje
Old Dutch: *ēcorno
Middle Dutch: êencōren
Dutch: eekhoorn
Old High German: eihhorno, eihhurno
Middle High German: eichurne
Alemannic German: Eichhore
German: Eichhorn
⇒ German: Eichhörnchen
⇒ Hunsrik: Eichhernche
Old Norse: íkorni
Icelandic: íkorni
Faroese: íkorni
Norwegian:
Norwegian Bokmål: ekorn
Norwegian Nynorsk: ekorn, ikorn
Old Swedish: ēkorne, īkorne
Swedish: ekorre, (dialectal) ikorn
Old Danish: īkærnæ
Danish: egern
Westrobothnian: ickȯrn, ikårn, ikkårn
Elfdalian: aikuonn
Jamtish: íkuðn
Gutnish: eikånn
Scanian: igarne
Bonus:
maniġfeald (manifold, many fold, of many parts)
Old English: maniġfeald, mæniġfeald
Middle English: manifald, monifald, manyfold, manifold
English: manifold, manyfold
Old Frisian: manichfald
Old Saxon: managfald
Old Dutch: *manigfald
Middle Dutch: menichvout
Dutch: menigvoud, menigvoudig
Old High German: manicfalt, manicfaltīg
Middle High German: manecvalt, manecvaltec
German: mannigfaltig
Old Norse: margfaldr
Icelandic: margfaldur
Norwegian: mangfoldig
Old Swedish: mangfalder
Swedish: mångfald, mångfaldig
Danish: mangefold
Gutnish: manggfaldur
Gothic: 𐌼𐌰𐌽𐌰𐌲𐍆𐌰𐌻𐌸𐍃 (managfalþs)
Hröð-
Anglo Saxon word of the day: Uhta
Anglo Saxon word of þe dæg:
ūhta (pre dawn) (last part of night)
Old English: ūht (< *unhtwaz), ūhta (< *unhtwô)
Middle English: *uht (found in compound uhtsang, uhtsong); Middle English: uhhtenn, uȝten, ughten, oughten (< Old English ūhtan, oblique form)
Old Saxon: ūhta
Middle Low German: uchte
German Low German: Uchte, Ucht
→ German: Uchte (“midnight mass”) (regional)
Old Dutch: *ūhto
Middle Dutch: uchte, ochte (various forms are attested, including nuchte through rebracketing, uchten/ochten from the case forms, and rarely uchtent/ochtent from the previous by analogy with avont (“evening”))
Dutch: ochtend
Old High German: uohta (irregular); *ūhta
Middle High German: uohte, ūhte (both rare)
German: Ucht, Aucht (both only in placenames and compounds)
Old Norse: ótta
Icelandic: ótta
Norwegian Bokmål: otte
Westrobothnian: ótt’
Old Swedish: ōtta, ōta
Swedish: otte, otta
Danish: otte
Gothic: 𐌿𐌷𐍄𐍅𐍉 (ūhtwō)
Bonus:
Lagustrǣt (ocean) literally “Water-road”.
Old English: strǣt, strēt
Middle English: strete, streete, stret, strate, street, stræt
English: street
Scots: street, streit, stret
→ Breton: straed
→ Cornish: stret
→ Welsh: stryd
→ Old Irish: sráit (see there for further descendants)
→ Old Norse: stræti (see there for further descendants)
Old Frisian: strēte
North Frisian:
Föhr-Amrum: struat
Mooring: stroote
Saterland Frisian: Sträite
West Frisian: strjitte
Old Saxon: strāta
Middle Low German: strâte
German Low German: Straat, Stroot
Old Dutch: strāta
Middle Dutch: strâte
Dutch: straat (see there for further descendants)
Limburgish: sjtraot, straot
Old High German: strāza
Middle High German: strāze
Alemannic German:
Swabian: Schdrôs
Bavarian: Stråßn, Strossn
Apeltonerisch: Streoss
Mòcheno: stros
Upper Bavarian: Straß
Central Franconian: Stroß
Eifel: Strooß
Hunsrik: Stros
Luxembourgish: Strooss
German: Straße
Rhine Franconian: Schdrooß
And
West Germanic: *lagu
Old English: lagu, lago
Middle English: laȝe, lawe, laie, leye
English: lay
Old Saxon: lagu
Old Norse: lǫgr
Icelandic: lögur
Faroese: løgur
Norwegian Nynorsk: log
Norwegian Bokmål: låg
Old Swedish: lagher
Swedish: lag
Old Danish: low, lou
→ Scots: lyog
Gothic: *𐌻𐌰𐌲𐌿𐍃 (*lagus) (> 𐌻𐌰𐌰𐌶 (laaz))
Hroð-
Book of the month (June)

Hilda Roderick Ellis Davidson is quickly becoming a favorite author of mine. Great detail and everything kept in context. I do love comparatives though I am biased.
Hrøð-
Rūnes of Þæs Dæġ (Beorc)
Rune of þē dæġ: (Beorc)Beorc: ᛒ᛬ Modern “B”. Birch Tree.
(Purity, Birth, Becoming, Reward)
A Rune of seeds sown, rewards earned through past effort and is often seen as a positive Rune in divination. The Birch is one of the first tree species to repopulate Northern Europe and Scandinavia after the last glacial maximum. It is not to be confused with the Poplar/Salicaceae (Aspen) as they are not actually a related species. Birch is in the family Betulaceae (Alder,Birch,Hazel,Hornbeam) and closely related to the Beech/Oak family. Aspen are of the Salicaceae family or Poplar (Aspen, Cotton Wood, Willow) The Anglo Saxon Rune poem confuses this distinction in the line:
“Beorc” byþ bleda leas, bereþ efne sƿa ðeahtanas butan tudder, biþ on telgum ƿlitig,heah on helme hrysted fægere,geloden leafum, lyfte getenge.
The “poplar” bears no fruit; yet without seed it brings forth suckers, for it is generated from its leaves. Splendid are its branches and gloriously adorned its lofty crown which reaches to the skies.
Note that the line clearly shows in OE “Beorc” but is translated as Poplar when the word for a Poplar is Æspen in OE. I am not sure why the translation is presented in this way. The fact two words exist in OE describing two different trees leads me to believe the confusion is not from the ancient source.

Hroðbeorht-
Anglo Saxon word of þē dæġ part 2: ǽrmorgen
Part 2.
ǽrmorgen (early morning)
Bonus word/name: Ælfréd (elf-counsel/wise counsel)
Famous example:
Ælfréd (Alfred the Great) king of the West Saxons. Son of Æðelwulf and Osburh.

ᚺᚱᛟᚦᛒᛖᚱᚺᛏ-
BALIS RUNA Hand crafted items!
Nicely crafted items spanning several themes including Germanic Norse folklore.
Please check out the following Etsy.com Seller BalisRuna
https://www.etsy.com/shop/BalisRuna
Please visit this Great Etsy.com seller for great Runic necklaces, charm boxes and other unique items.
I own a few items, great energy and spirit.
Cheers!
Hroberht-
Who are the Norse people (History/Culture post)
The Norse/Germanic people : A brief history:
The history of the Nordic people begins in Central Asia and the Russian steppe when the Indo-Europeans start migrating west into modern-day Europe. During the great migration a branch of the IE moved into present day Scandinavia and became isolated most likely due to climate disruptions. Human beings have occupied Scandinavia for at least 11000 years. It is in the forest and frozen mountains that the Nordic people get the distinct cultural/linguistic identity known as Germanic. After developing a unique culture the Germanic people begin moving south for less turbulent weather and cross the Baltic and North seas into Germany, Poland and Jutland. The migration age tribes founded the modern Nordic countries we know today like Scandinavia (Norway-Sweden-Denmark), Germany and England to name a few.
The culture of the Norse was actually already 1000 years or older when the Viking age began and a new wave of Germanic people again started crossing into Europe and Britain carrying largely the same migration age culture, legal systems, Runic codex and religious beliefs as the previous migrating tribes. Some of the identifying markers of Nordic culture is complicated knot work, exceptional metal/wood work, seafaring/boat building and design, metaphoric poetry and spoken word, grand feasting halls, ancestral worship and equal rights for women. A fact reviled by Roman authors when facing the Teutons in the Alpine regions during the migration age. I use the term Norse as a general description of the larger Germanic culture from its Dutch origin “Noors” “People from the north” because Germanic culture originates in Scandinavia/Denmark.
Runes:Glossary:
We Norsemen have an indigenous alphabet called Runes or the Elder Futhark, The header of my blog is in Anglo-Saxon Futhorc set and many variations exist as the system evolved out of the Elder Futhark. Runes were typically used for marking ownership such as Hermeric owns this knife or Olaf is buried here but many large inscriptions do exist. Each sign also has a divine meaning with immense power behind it. I have often called the Runes the language of the universe. I personally believe in the power behind the Runes. The origin of the Futhark is a mystery, theories exist but none satisfy in explaining the origin. It was largely accepted that a Mediterranean origin like Etruscan might explain it but no early finds exist near the Mediterranean, they all exist in Denmark , Northern Germany and Scandinavia. Now it is theorized that Western Germany/Denmark may be the original zone of expansion and Scandinavia being less explored has some very old inscriptions and “could” be the originator of the Runic script. Some have linked the Runes with the Hallristningar symbols carved in Neolithic Sweden/Norway which adds a new layer of age and interest to the story. The divine description in the Norse Lore is that Allfather Odin pulls them from Ginnungagap as he is hanging from Yggdrasil. A full article on Runic origins and theory will be presented in an upcoming post.
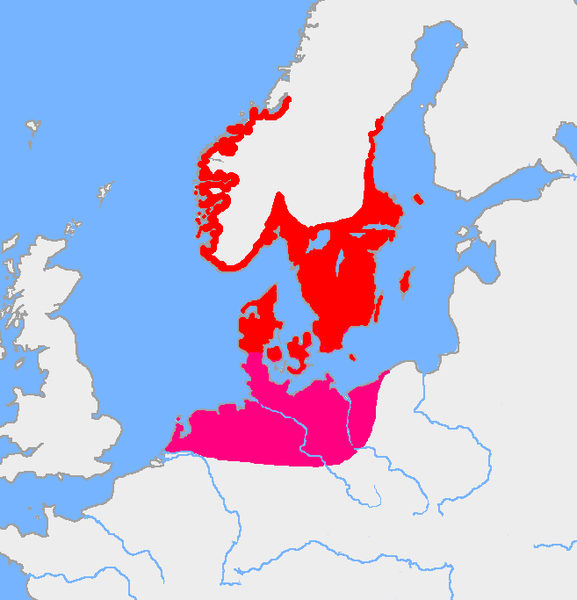
Sites of Elder Futhark discovery in Europe. Common Germanic would be the language. All German languages were mutually intelligible at this time.
Geography:

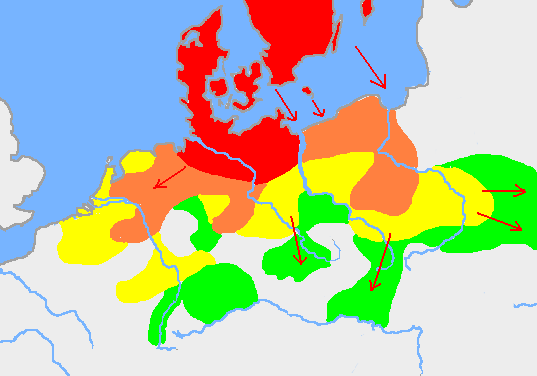
Nordic Bronze Age. 1700-500 BC
Pre-Roman Iron Age in Germania/Scandinavia 5th/4th – 1st century BC
Germanic Migration 750BC-1AD.
Red= Before 750 BC
Orange= New settlement by 500 BC
Yellow= New settlement by 250 BC
Green= New settlement by 1AD.
………………………………………………………………..
Stone Age Connection to Germanic Culture:
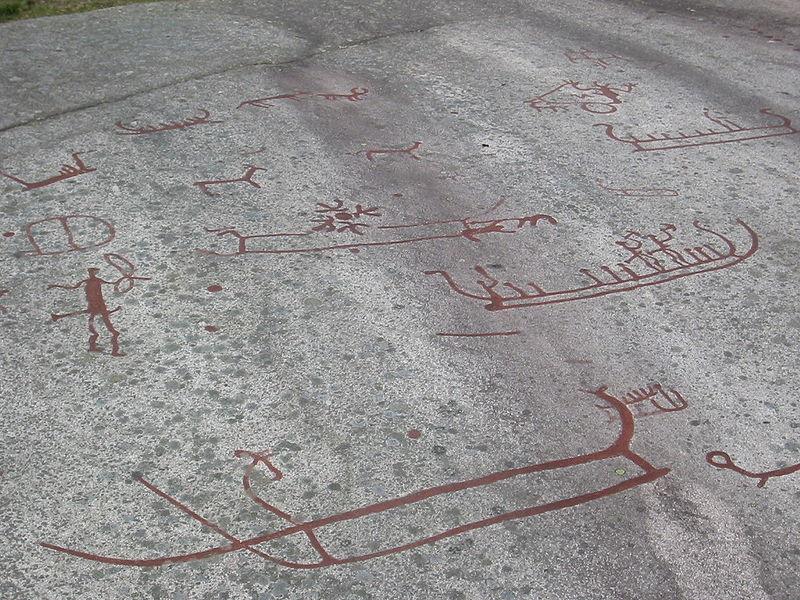
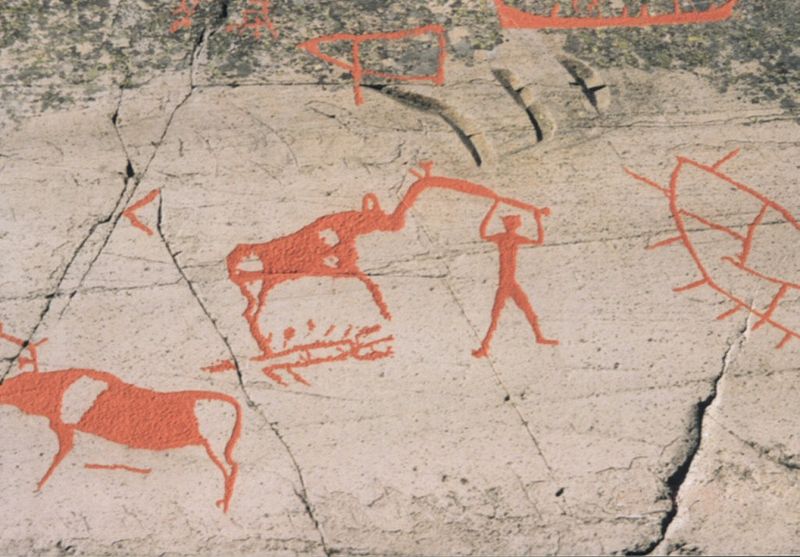 Stone Age Carving from Norway.
Stone Age Carving from Norway.
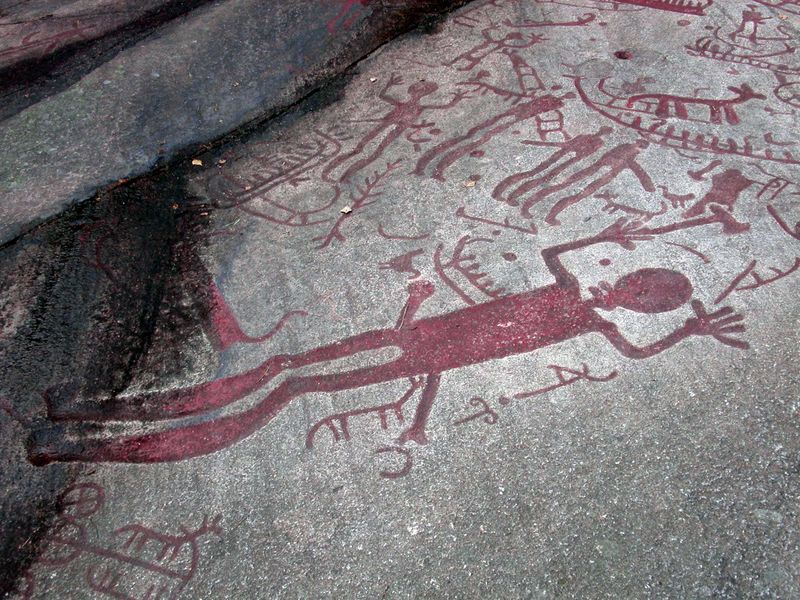
Complex Nordic Bronze age carving of obvious similar creation as the design above.
Rock carving form Norway (Over 6000 years old) Showing unique artistic elements.
Norway 1200BC
Many images on these stones dating from 6000 years ago tothe Iron age depict many traditions found in Germanic and later Viking age culture such as waging war on boats, farming/herding, fishing, ship design, beings in Germanic religion and symbols found throughout Nordic culture prehistoric to modern. When looking at these images one could understand how the Runes may have evolved out of it stylistically. The exact culture responsible is unknown in some cases but elements can be traced to later Nordic customs.
STONE CARVING PHOTO’S ARE FROM WIKIPEDIA. Copyright to respective owners.
A small gallery of images and symbols. Art of my own creation is marked.

Irminsul: Ancient German totem most likely of Yggdrasil (World tree) Symbol is associated with The Saxons and a Deity called Irmin who is most likely Odin under one of his alias/regional names. (Photo by Varus111) Reconstructed Irminsul in Hildesheim Germany.

Thor-Thunor: Nordic Thunder God. Viking age bronze statue.
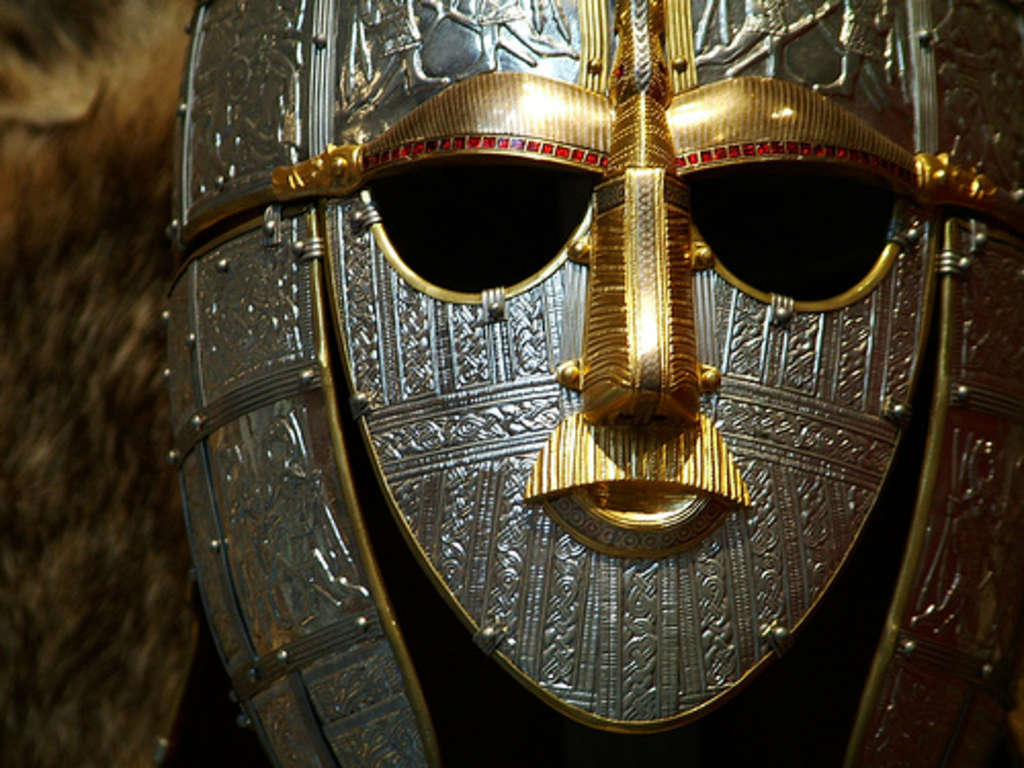
Helmet replica from the Sutton-Hoo find. Adorned with glorious plates referencing Nordic customs, legendary figures and amazing detailed metal work. (Not my photo)
Stone carving designs from Gotland Sweden. Copyright Call Of Steel 2012.
Gotland Sweden Stone Carving: Pre Viking. Copyright COS 2012.
Viking age stone carving from Gotland Sweden:Viking age. Copyright COS 2012.
Anglo Saxon decoration. Copyright COS 2012.
…………………………………..
In summary I hope this post gave at least some idea of Norse culture. It is near and dear to my heart as I descend from these mighty folk and try as an artist to keep some element of the old ways alive and well into the future.
Thanks for reading and stay tuned for more Blacksmith and historical posts.
Hroðberht-